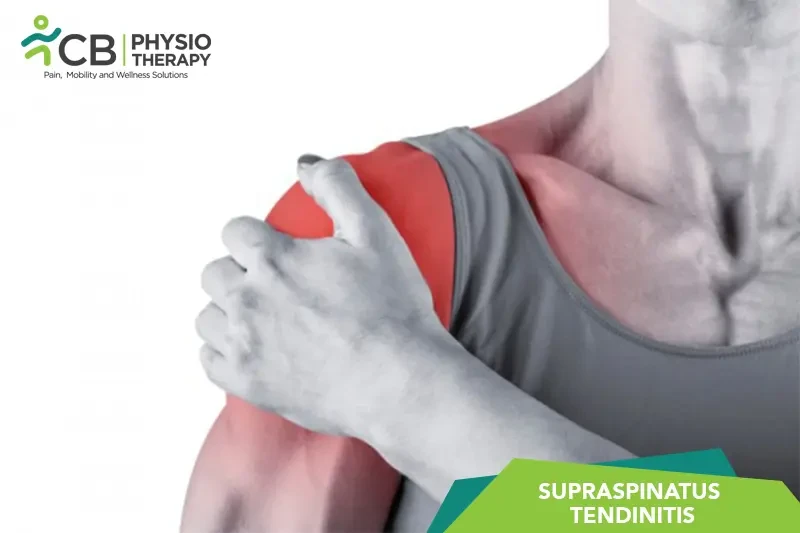
Rest: The patient is advised to rest and asked to avoid activities that exacerbate pain, particularly overhead movements.
Cryotherapy: Apply cryotherapy (ice packs) to the shoulder for 15-20 minutes several times a day to reduce inflammation and pain.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS):TENS provides pain relief by delivering low-voltage electrical currents to the affected area.
It works by stimulating sensory nerves, which can help block pain signals to the brain and promote the release of endorphins, the body's natural painkillers.
Ultrasound Therapy:Ultrasound Therapy promotes tissue healing and reduces pain and inflammation. Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to generate deep heat within the tissues, enhancing blood flow and promoting the healing process.
Interferential Current Therapy (IFC):IFT reduces pain and inflammation and improves muscle function. IFC uses medium-frequency electrical currents that intersect to create a low-frequency current that penetrates deeper into the tissues.
Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS):EMS prevents muscle atrophy, improves muscle strength, and enhances blood circulation.
It delivers electrical impulses that cause muscle contractions, which can help maintain muscle tone and improve circulation.
Therapy (Low-Level Laser Therapy - LLLT):Laser Therapy (Low-Level Laser Therapy - LLLT reduces pain and inflammation and promotes tissue healing. LLLT uses low-intensity laser light to penetrate the tissues and stimulate cellular processes, enhancing tissue repair and reducing inflammation.
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy (PEMF):Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy (PEMF) reduces pain and inflammation and promotes healing. PEMF uses electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular repair and improve circulation.
Iontophoresis:
Iontophoresis is used to deliver anti-inflammatory medications directly to the affected area through the skin. It uses a low electrical current to drive medication (such as corticosteroids or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) through the skin to the underlying tissues.
Gentle Range of Motion Exercises:1: Pendulum Exercises: To keep the shoulder joint mobile without stressing the tendon.
2: Passive Range of Motion Exercises: Assisted movements to maintain flexibility.
Stretching Exercises:1: Posterior Capsule Stretch: To improve shoulder flexibility.
2: Cross-Body Shoulder Stretch: To stretch the posterior shoulder muscles.
3: Doorway Stretch: To stretch the anterior shoulder and pectoral muscles.
Strengthening Exercises:1: Isometric Exercises: Gentle muscle contractions without joint movement.
2: Resistance Band Exercises: Gradual introduction of resistance to strengthen the rotator cuff and surrounding muscles.
3: Scapular Stabilization Exercises: To improve shoulder blade control and function.
Manual Therapy:1: Soft Tissue Mobilization: To reduce muscle tension and improve circulation.
2: Joint Mobilization: To enhance joint movement and decrease stiffness.
Advanced Strengthening Exercises:1: Weight Lifting Exercises: Gradual progression with weights to build muscle strength.
2: Plyometric Exercises: For those returning to sports, to improve power and coordination.
Functional Training:Sport-specific or activity-specific exercises to prepare for return to normal activities.
Proprioceptive Training:Exercises to enhance shoulder stability and joint awareness, such as using balance boards or performing exercises on unstable surfaces.
Ergonomic Adjustments:Adjusting workspaces, sports techniques, and daily activities to reduce strain on the shoulder.