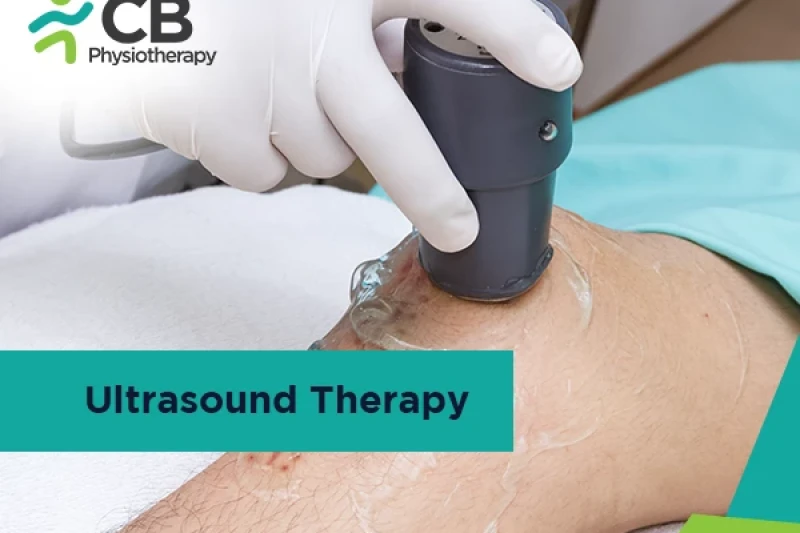
This therapy involves the application of Ultrasound waves above the range of human hearing to treat various types of injuries. The application of Ultrasound Therapy helps in increasing the blood flow of a localized area to reduce the swelling and inflammation in that area. It is also used to enhance the healing of a bone fracture.
It is generally categorized into 2 types:
1. Thermal Ultrasound Therapy
This therapy involves the continuous transfer of sound waves resulting in small vibrations in the deep tissue molecules. These vibrations increase heat and friction in the molecules. This heating effect results in increases in the metabolism of the tissue cells resulting in the healing of the soft tissues.
The local rise in the temperature could be used to accelerate healing. It is generally used in cases of Myofascial pain, muscle strain or sprain, scars, or adhesion.
2. Mechanical Ultrasound therapy
This therapy uses a single vibration of sound waves to penetrate tissue. It causes the expansion and contraction in the tiny gas bubbles of the soft tissues which then helps to reduce the inflammation, reducing tissue swelling and thus decreasing pain in the tissue.
It is generally used if you have Pain and Swelling such as with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome,
Ultrasound may be used in a continuous mode where the treatment head continuously produces ultrasonic energy or pulsed where the treatment head continuously produces ultrasonic energy or pulsed where the periods of ultrasound are separated by periods of silence.
Ultrasound therapy involves the use of a metallic probe. The procedure begins with the application of gel either on the head of the probe or directly to the skin. This gel helps the sound waves to penetrate the skin evenly. After the gel is applied, this probe is then continuously moved over the selected area for over 5 to 10 min. The intensity or the power of an Ultrasound is adjusted as per the desired effect. Some people may feel a mild pulsing during this therapy while others may feel a slight warmth in the selected area.
Ultrasound Therapy has numerous benefits as it can be used for a vast range of issues. However its most commonly used for:
1: Heating and relaxing the muscles to alleviate the pain.
2: Increasing the blood flow i.e. lymph (lymph: a fluid that carries white blood cells throughout the body) to enhance the healing process not only of muscles but also joints and ligaments.
3: Softening of any existing scar tissue.
4: A low-intensity Pulsed Ultrasound (LIPUS) is used for fracture repair.
5: Management of the Knee Osteoarthritis (OA)
The most common conditions that can be treated using Ultrasound therapy are:
1: TENDONITIS / TENDINITIS:
It is a general term that is used to define the inflammation of the tendon tissue that connects the muscle to the bone. This is the most common cause of soft-tissue pain. It can occur at any age but it is more common in adults who do a lot of sports. Old-age people are also prone to it as the tendons tend to lose their elasticity and become weaker with age. Its common types are:
1: Tennis Elbow
2: Golfer's Elbow
3: Tendinitis (Achilles, Wrist, supraspinatus, bicipital)
4: Jumper's Knee
5: Swimmer's Shoulder
6: Trigger Finger or Thumb
7: Ganglion
2: Other conditions that can be treated with Therapeutic Ultrasound are:
1: Joint Swelling
2: Muscle spasm
3: Pain
4: Fractures
5: Muscle or ligament injury(ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL, etc )
6: Sprains and Strains ( ankle, knee, lower back, etc)
7: Knee Bursitis
8: Osteoarthritis
9: Rheumatoid arthritis
10: Myofascial pain
11: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
12: Low back pain
13: Phantom Limb Pain
14: Varicose ulcers
15: Herpes zoster
16: Pressure sores
17: Frozen shoulder
18: Temporomandibular joint disorder
19: Prolapsed intervertebral disc
20: Dupuytren's contracture
21: Meniscal injury
Select your City to find & connect with our experts regarding Physiotherapy for Ultrasound Therapy