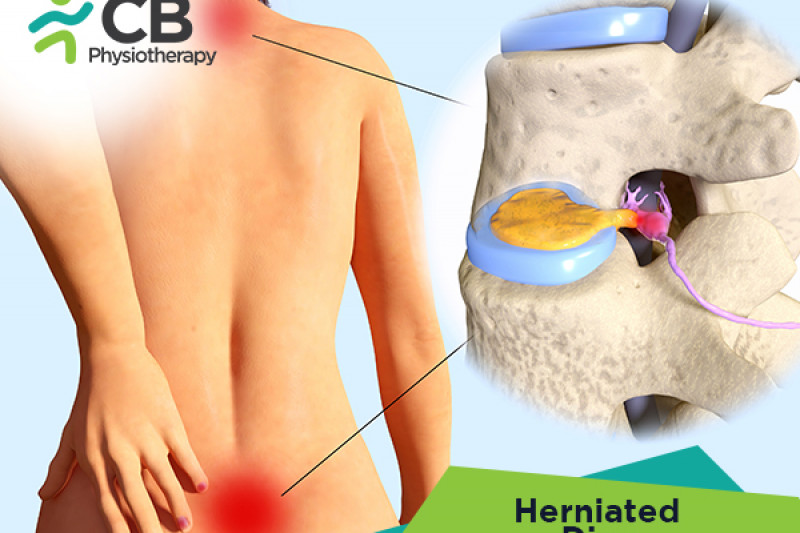
Herniated disc or slipped disc is a problem that occurs in the rubbery cushions or discs which lie between the vertebrae bones that form the spine. A spinal disc has a soft, jellylike center known as the nucleus fibrosis surrounded by a tougher, rubbery exterior known as the annulus fibrosis. Certain movements may also cause a slipped disc. A disc can slip out of place due to excessive strain on the lower back, resulting in a slipped disc. A herniated disc occurs when some of the nuclei are pushed out through a tear in the annulus, this can occur in any part of the spine resulting in irritation of the nerve.
Herniated disc or slipped disc can occur at any part of the spine, from the neck to the lower back. The lower back is the most common area for a herniated disc. Symptoms vary from person to person few of the symptoms are listed below:
A slipped disc occurs when the annulus of the outer ring becomes weak and the inner part moves out. A disc can slip out of place, due to the following reasons
Physical examination
Physical examination is done to look for the source of the pain and discomfort. Also involves checking the nerve functions and muscle strength, and whether the pain is felt while moving or touching the affected area. Aggravating and relieving factors are noted with medical history.
X-rays:
The X-ray can help show any bony problem and thus rule out other conditions with similar symptoms
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan helps to show the location of the disk and the affected nerves.
Discograms:
Discogram involves injecting dye into the center of the disc, this helps to show cracks in the disc. It shows whether a herniated disc is exerting any pressure on the spinal cord and nerves.
Myelogram:
Myelogram is done by injecting dye into the spinal fluid and then taking an x-ray image.
Medications: Anti-inflammatory, Analgesics, muscle relaxers, opioids.
Note: Medication should not be taken without the doctor's permission.
Surgery:
In a few cases, where pain doesn't subside for a prolonged period, surgery is recommended to relieve the pressure on the nerve endings.
Cryotherapy is used as it reduces inflammation and pain.
Thermotherapy is used to promote blood flow and remove toxins.
Collar:
Collar can be used for short-term support for the neck or lower back.
Massage therapy:
Massage therapy can be given to improve blood circulation and decrease inflammation.
Ultrasound uses sound waves to stimulate the affected area and thus improves blood flow to the part.
Transcutaneous electrical stimulations (TENS):
Transcutaneous electrical stimulations (TENS) promotes gentle relaxation.
Interferential therapy is used to reduce pain and inflammation.
Traction:
Traction reduces the weight on spinal discs, helps alleviate pressure on the affected nerve, and thus relieves pain.
Laser therapy helps to enhance the healing process, decrease pain and increase mobility.
Manipulation and mobilization:
Manipulation and mobilization techniques are used to break the adhesions, properly align the bones and thus improve mobility.
Strengthening and stabilization exercises:
These exercises improve core muscle strength and support for the back. For a sore back strengthening exercises are done for the trunk and all layers of the core muscles which helps to support the low back and prevent excessive strain through the discs.
Stretching exercises:
Stretching exercises are done to improve the flexibility of the back muscles.
Balance exercises:
Balance exercises are taught for awareness to show how the back should be while moving during various activities.
The patient is advised to avoid the activities which aggravate the symptoms like forward bending and prolonged sitting can increase the pressure on the disc and thus aggravate the condition. Lifting heavy objects, sudden twisting and turning movements that lay stress on the back should also be avoided.
Select your City to find & connect with our experts regarding Physiotherapy for Herniated Disk Or Slipped Disc