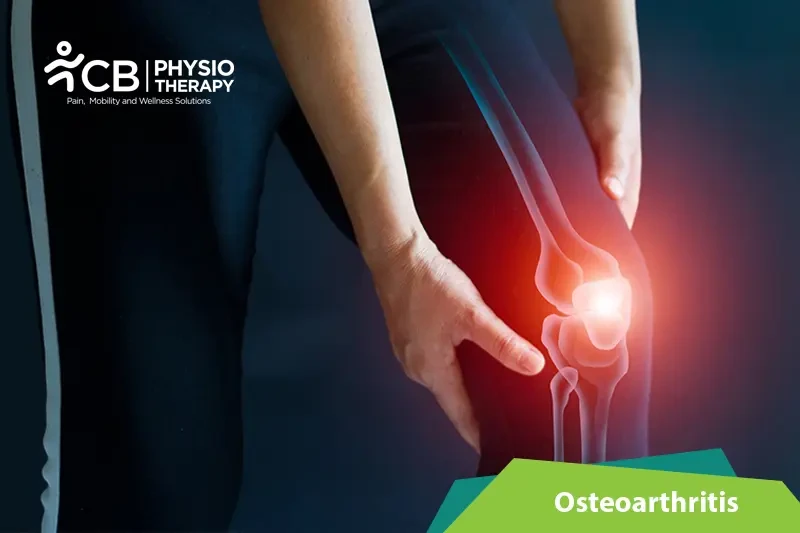
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease. It is the most common joint disease and is considered to be the leading cause of disability in older adults. Osteoarthritis is characterized by progressive deterioration and loss of articular cartilage with the simultaneous proliferation of new bone, cartilage, and connective tissue.
Pain is the most common symptom of Osteoarthritis, other symptoms may include:
There is no specific cause of Osteoarthritis, but factors that can be responsible for the development of the disease, include:
Pathology:
Osteoarthritis is a progressive degradation of the cartilage, due to a combination of mechanical, inflammatory, and metabolic factors affecting the hyaline cartilage, the subchondral bone, the joint capsule, and the synovium as well as the surrounding ligaments. The synovium becomes thick and the subchondral bone begins to remodel forming lytic lesions.
Physical examination:
Examiner checks the family and medical history of the patient. Physical examination is done to evaluate the location of pain, swelling, range of motion, strength of muscles, and balance.
X-rays:
X-ray creates detailed images of bones. X-rays of an osteoarthritic joint may show changes in the bone, loss of joint space, and formation of marginal osteophytes.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used to detect damage to the muscles, ligaments, and tendons.
Bone scan:
A bone scan also helps to determine the condition of the bone and soft tissues of the joint.
Medication: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), analgesics, corticosteroids.
Note: Medication should not be taken without the doctor's prescription.
Surgery:
Surgery is recommended if the patient has debilitating pain and major limitation of functions such as the impaired ability to work or sleep, daily activity, or impaired ability to walk.
Cold therapy or cryotherapy causes numbness resulting in the constriction of blood vessels, thus reducing swelling.
Thermotherapy transfers heat to the connective tissue and muscles, which improves blood flow, removes toxic substances, and decreases pain. It also improves flexibility which leads to improvement in range of motion.
Ultrasound therapy uses sound waves to decrease spasms and reduce joint stiffness.
Transcutaneous electrical stimulations (TENS):
Transcutaneous electrical stimulations (TENS), transmits electrical stimulations through pads placed on the skin, to relieve pain.
Interferential current therapy (IFT), is an electrical modality that is used to decrease pain and increase mobility.
Hydrotherapy:
Water exercises are useful when the weight-bearing joints are affected, these exercises increase the range of motion by immersing the body in water and allowing weight-bearing muscles to relax, and alternatively, a simple range of motion exercises are performed.
Manual therapy involves several techniques and stretches to increase the quality and range of movement of the ankle.
Progressive resisted exercises:
Strengthening exercises consist of Progressive resisted exercises, and strong and sustained repeated sessions of isometrics exercises.
Range of motion exercises:
Active free relaxed rhythmic movements are done to improve the range as well as promote relaxation of the joint. Relaxed passive movements are started to mobilize stiff joints. Range of motion exercises causes improvement in functional independence.
Assistive devices:
Assistive aids, modified supports, orthoses, adaptations, and modifications in the environment are recommended which prove to be beneficial for the patients.
Strengthening Exercises:
Strengthening exercises are taught to restore strength and endurance. These exercises can involve the use of weight cuffs, dumbbells, resistance bands, and cardio exercise equipment such as treadmills or static cycles.
Progressive resisted Exercises:
Strengthening exercises consist of Progressive resisted exercises, and strong and sustained repeated sessions of isometrics exercises.
Stretching exercises:
Stretching exercises are done by gently lengthening the muscles around the joint. Regular stretching increases the range of motion and flexibility.
Aerobic Exercises:
Aerobic exercises like cardio exercises, like speed walking, running, vigorous swimming, stationary bike, etc can also be done without stressing the joints.
The patient is advised to decrease high-impact activities in daily life and minimize the stress on the joint. The patient is also encouraged to reduce weight, which can be achieved through a combination of diet and exercise.
Select your City to find & connect with our experts regarding Physiotherapy for Osteoarthritis