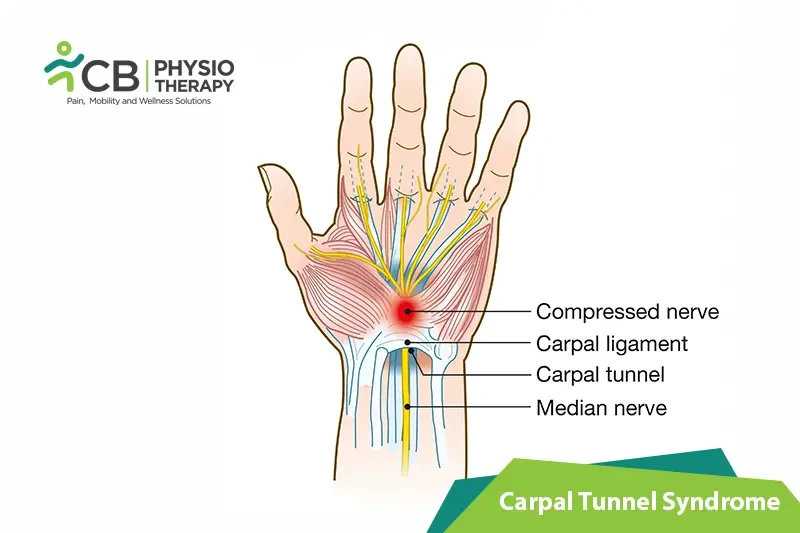
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that affects both the hand and arm. It is the most common entrapment neuropathy caused by the compression of the median nerve as it travels through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. A Carpal tunnel is a passage in the wrist through which the median nerve runs to end in hand. Early symptoms include pain, numbness, and tingling when the median nerve is compressed or squeezed in the wrist. The median nerve provides sensation to the index, middle, and ring fingers and also controls the muscles around the base of the thumb.
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome begin gradually or come and go at first. But when the condition worsens, the symptoms may become more frequent or persist longer. When the contents of the carpal tunnel, like the median nerve, blood vessels, and tendons, enlarge they take up space in the tunnel and eventually crowd the nerve. This causes increased pressure on the nerve and causes carpal tunnel symptoms.
Symptoms include:
Pathology:
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is an entrapment neuropathy of the median nerve. Carpal tunnel is located at the base of the palm, bounded on 3 sides by carpal bones and anteriorly by the transverse carpal ligament. Inside this tunnel there runs the median nerve, the flexor tendons, and their synovial sheaths. Hypertrophy or edema of the flexor synovium causes compression of the median nerve at the wrist. This can cause physical damage to the nerve resulting in pain, numbness and weakness, etc.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused due to pressure inside the tunnel which becomes too high and compresses the median nerve as it passes through the narrowed tunnel. It occurs due to:
Physical examination:
A complete examination of the entire upper limb, including neck, shoulder, elbow, and wrist, to exclude other causes. Initial inspection of the hand and wrist can provide clues about the cause. The patient is examined for sensation to pain, two-point discrimination, and soft tissue over the median nerve is examined for mechanical restriction, etc.
Carpal compression test:
A carpal compression test is done by applying firm pressure directly over the carpal tunnel for 30 seconds. The test is positive when paresthesias, pain, or other symptoms are produced.
Medication: NSAIDS, Diuretics, Oral steroids, Vitamin B6, Corticosteroid injections, etc.
Note: Medication should not be taken without a doctor's prescription.
Surgery:
Surgery is the treatment done for patients with severe median nerve damage, characterized by permanent sensory or motor loss, or axonal loss or denervation indicated by electrodiagnostic studies. Open carpal tunnel release (OCTR) and endoscopic carpal tunnel release (ECTR) are the two types of effective surgeries done for the patients.
Modification of activities and workplace:
Modification of activities and workplace is done which can be beneficial in controlling milder symptoms of CTS. For example, proper placement of the hand on the keyboard at a proper height and minimizing flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction of the hand when typing.
Ice therapy can be used by applying ice to the wrist for 10- 15 minutes once or twice an hour.
Heat therapy can be applied by immersing the affected hand in warm water moving the hand and wrist in the water.
Ultrasound therapy is used to break the adhesions, increase circulation and improve range of motion by using its fibrinolytic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-irritant action of the ultrasound.
Transcutaneous electrical stimulation (TENS):
Transcutaneous electrical stimulation (TENS) is highly effective to reduce pain and swelling.
Laser therapy is used to decrease pain and paresthesia. Laser therapy is also approved by the FDA for the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS).
Iontophoresis:
Iontophoresis is also found to be effective as a treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Splinting and hand brace
The physiotherapist advises the patient to take sufficient rest. Immobilization helps to eliminate active movements in the affected hand. The wrist is fixed in a neutral position so the tension in the carpal canal will be minimal and the carpometacarpal and the interphalangeal joints are fixed in slight flexion to achieve the same.
Manual therapy includes mobilization of soft tissue, carpal bone, and median nerve. It is a hands-on technique that helps to increase the mobility of the nerve. It also helps to improve the range of motion of joints that are affected by the carpal tunnel.
Massage therapy includes compression, cross-fiber function, deep tissue work, stretching, and trigger point. This therapy reduces pain, improves grip strength, and makes muscles more flexible.
Stretching exercises:
Stretching exercises include "Stretch Armstrong." In this exercise, the arms are placed in front (one at a time), spreading the fingers, and then "stretching the wrist and fingers as far as possible and then holding that position for 20 seconds. Basic wrist stretches include bending the hand towards the body so that the fingers point up toward the ceiling.
Strengthening exercises help to strengthen the hands and the grip. Hand exercises like hand squeeze exercises like squeezing a soft rubber ball and then holding the squeeze position for 5 seconds. The physiotherapist recommends 10 repetitions and 3 times a day. For the wrist, wrist curls are done by bending the wrist 30 times daily while the arm is bent like the letter L, and a wrist resistance exercise can also be done by raising one hand while the other hand is kept down.
Movement exercises:
Movement exercises consist of tendon gliding and nerve gliding. The tendon exercise consists of moving fingers through different positions like curling them inward till they're bent at the middle knuckles and straightened so that the hand is shaped like an L. Nerve exercise such as moving parts of the hand and wrist into different positions. Straightening the fingers out so that they point up, other exercises consist of bending the wrist so that the fingertips are pointed away from the body of the patient.
The patient is advised to avoid inappropriate and provoking positions, and continue strengthening and mobility exercises to help the affected arm recover. The patient is also educated on how to manage the carpal tunnel symptoms and modify the daily activities to reduced repetitive movements that aggravate pain.
Select your City to find & connect with our experts regarding Physiotherapy for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (cts)