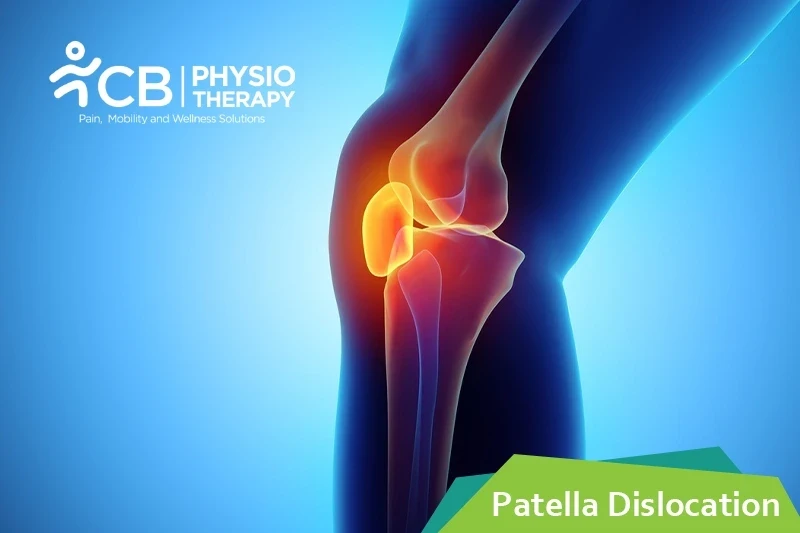
Patella dislocation is a dislocation of the kneecap i.e the patella from its groove at the knee joint. The knee joint is a joint at which three bones meet the thighbone, the shinbone, and the patella. Normally, when the knee is bent and straightened, the kneecap slides up and down inside a groove, which is between the bottom end of the thighbone and the upper end of the shinbone, this groove is known as the trochlear groove. When the patella dislocates, it's forced out of the trochlear groove and can no longer move up and down. This locks the knee pulls the ligaments (that secures the knee joint) out of place and often tears them. Patella dislocation is an acute injury caused by force. It is a common injury since the kneecap takes less force to dislocate.
Patellar dislocation can occur due to many reasons, a few of them are mentioned below:
It depends on how far the patellar bone has been forced out of the knee joint, and to what extent the surrounding muscles and ligaments, blood vessels, and nerves have been injured. The symptoms include:
PATHOLOGY
Patella dislocation is influenced by minor alterations or derangements factors. The sulcus angle should not be more than 138 degrees and the Q angle should not exceed15 degrees. Both patella Alta and the weakness and atrophy of the vastus medialis obliquus, influences the dislocation tendency and may cause muscular imbalance.
Physical examination:
Physical examination of the knee is done thoroughly to check the dislocation, joint effusion, and bleeding. The patient is assessed for femoral anteversion, tibial torsion, patellar Alta, genu recurvatum, genu valgus, genu varum, etc.
X-ray:
X-ray helps to show dislocation, fracture, malalignment, loose bodies, arthritic changes, it also helps to exclude associated fractures like osteochondral, avulsion, etc.
Computed Tomography:
Computed Tomography helps to measure the distance between tibial tuberosity and trochlear groove.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a gold standard and helps to check dislocation and the degree of tear.
Medication: NSAID's, pain killers, muscle relaxants, etc.
Note: Medication should not be taken without a doctor's prescription.
Reduction:
Reduction is a process of manually relocating the kneecap.
Surgery: In case of damage to the bone or the cartilage and tendons of the knee, surgery is recommended. Types of surgeries include:
Elevation:
The affected limb is kept in an elevated position to help keep the swelling down.
Bracing:
Bracing is done to help control the position of the patella by preventing dislocation but care should be taken that the brace should not be overused.
Cryotherapy helps to decrease swelling and pain.
Thermotherapy is used for relaxation of the muscles which in turn helps to perform the exercise program.
Ultrasound is very effective in breaking adhesions and improving flexibility.
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS):
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation provides relief from pain, which may occur after performing stretching exercises.
Laser therapy is used for the pain management of patients having dislocation of the patella.
Kinesio-taping helps reduce the movement of the patella, it holds the patella in the proper position while the muscles around the knee work properly to hold the patella in position.
Manual therapy consists of different techniques like manipulation, joint mobilization, and soft tissue mobilization. It helps in decreasing pain and improves functional mobility of the knee joint.
Range of motion exercises:
Range of motion exercises help to improve the contraction of the knee muscles. These exercises are very important to improve the flexibility of the muscles while the joint is restabilized. Pelvic stabilization exercises help strengthen the hip flexors and hip abductors, which helps to stabilize the function of the extremity.
Strengthening exercises like quadriceps, hamstrings, adductors, hip, and lower abdomen are recommended. Closed kinetic chain exercises are also done. Advanced hip strengthening is done after a few weeks to help the patient prepare to return to normal activity.
Stretching exercises:
Stretching exercises improve the flexibility of hamstrings and quadriceps. These exercises are essential to ensure that each muscle group is offering the full range of mobility.
Proprioception and balance exercises:
Proprioceptive and balance exercises are also incorporated in the exercise program to improve the stability and balance of the knee.
Gait training:
Gait training is given gradually with crutches and a brace to hold the joint in place.
The patient is advised to continue doing the exercises for a lifelong. If he/ she is an athlete, then he/ she needs to practice vigorous movements and exercises and should be done properly. Incorrectly doing the exercises can put repetitive stress on the muscles and joints.
Select your City to find & connect with our experts regarding Physiotherapy for Patella Dislocation