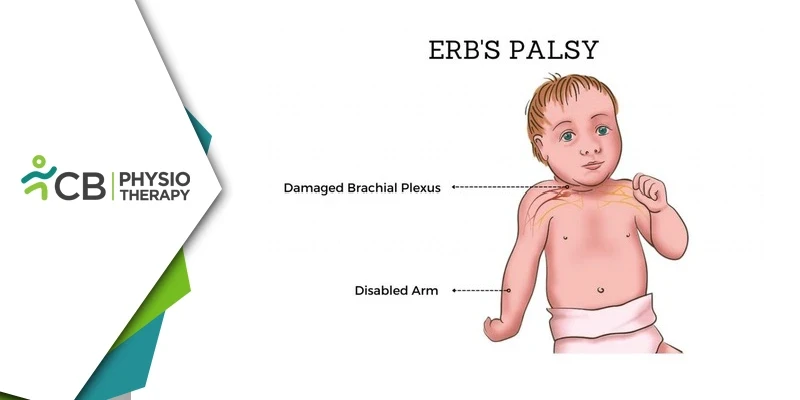
Erb’s Palsy, also known as brachial plexus birth palsy, is a condition that occurs due to damage to the brachial plexus nerves during childbirth. This condition primarily affects the movement and sensation in the upper arm and shoulder. While physical therapy plays a critical role in the rehabilitation of individuals with Erb’s Palsy, electrical stimulation (E-stim) has emerged as an effective adjunct therapy to promote recovery. This blog explores the mechanisms and benefits of electrical stimulation in the management of Erb’s Palsy.
Understanding Erb’s Palsy
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that extends from the spinal cord in the neck to the arm, enabling movement and sensation in the upper limb. In Erb’s Palsy, the upper roots of this nerve network (C5 and C6) are affected due to excessive pulling or stretching during childbirth, often caused by difficult deliveries, prolonged labor, or improper handling. Erb's Palsy varies depending on the severity of the injury, the symptoms include weakness in the affected arm, loss of sensation, limited range of motion in the shoulder or elbow, and muscle atrophy over time due to disuse.What is Electrical Stimulation?
Electrical stimulation involves delivering controlled electrical impulses to muscles or nerves using specialized devices. These impulses mimic the natural signals the nervous system sends to activate muscle contraction. In the context of Erb’s Palsy, E-stim is employed to prevent muscle atrophy, re-educate muscles by promoting contraction, improve circulation, and reduce stiffness.Several forms of E-stim, such as neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES), functional electrical stimulation (FES), and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), are utilized depending on the therapeutic goals.
Benefits of Electrical Stimulation:
1. Muscle Re-EducationIn Erb's Palsy, weak muscles can lead to compensatory movement patterns and further functional decline. E-stim helps re-educate muscles by facilitating proper contraction and improving the motor control needed for movement.
2. Prevention of Muscle Atrophy
Due to nerve damage, the affected muscles may not receive adequate neural input, leading to atrophy. E-stim activates these muscles artificially, preserving their size and strength during recovery.
3. Promotion of Nerve Regeneration
Although nerve regeneration is a slow process, E-stim enhances the environment for nerve repair by improving circulation, reducing inflammation, and stimulating dormant nerve fibers.
4. Enhanced Blood Circulation
E-stim increases local blood flow, which delivers oxygen and nutrients to the affected area. This facilitates healing and reduces stiffness in the joints and soft tissues.
5. Enhanced Motor Learning:
When paired with task-specific training, functional electrical stimulation (FES) enhances motor learning and improves coordination in affected limbs.
Types of Electrical Stimulation Used in Erb’s Palsy
1. Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES)NMES is the most commonly used form of electrical stimulation in Erb’s Palsy. It activates specific muscle groups by targeting motor nerves, thereby improving strength and functionality. NMES is typically applied to the deltoid, biceps, and other muscles weakened by nerve damage. Enhances voluntary muscle control, prevents atrophy, and supports joint stability.
2. Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
FES goes a step further by integrating muscle activation into functional tasks such as reaching or grasping. Used in therapy sessions to assist with task-oriented movements. Improves coordination, promotes neuroplasticity, and facilitates independence in daily activities.
3. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
Although TENS is primarily used for pain relief, it can also reduce discomfort and stiffness in Erb’s Palsy. Electrodes are placed near the affected area to deliver low-frequency electrical impulses. Alleviates pain, reduces muscle spasms, and improves overall comfort.
Challenges and Limitations of Electrical Stimulation
While E-stim is a powerful tool, it is not without challenges:1: Skin Sensitivity: Some individuals may experience redness or irritation at electrode sites.
2: Compliance Issues: Ensuring consistent use, especially in pediatric cases, can be challenging.
3: Limited Efficacy in Severe Cases: In cases of complete nerve avulsion, E-stim may not be effective without surgical intervention.
Electrical stimulation has revolutionized the rehabilitation landscape for Erb’s Palsy by providing an effective, non-invasive, and targeted approach to recovery. When combined with physiotherapy and early intervention, it offers a powerful solution to improve muscle strength, prevent complications, and enhance overall functionality.
For individuals affected by Erb’s Palsy, electrical stimulation represents a beacon of hope, paving the way for improved quality of life and independence.