स्पोंडिलोलिस्थीसिस एक रीढ़ की हड्डी की स्थिति है जो स्पाइनल कॉलम के निचले कशेरुकाओं को प्रभावित करती है। यह रोग निचली कशेरुकाओं में से एक को उसके नीचे मौजूद हड्डी पर आगे खिसकने का कारण बनता है। यह एक दर्दनाक स्थिति है लेकिन ज्यादातर मामलों में उपचार योग्य है, दोनों चिकित्सीय और साथ ही शल्य चिकित्सा पद्धतियों द्वारा।
स्पोंडिलोलिस्थीसिस के लक्षण अलग-अलग होते हैं। हल्के लक्षणों से पीड़ित लोगों में कोई लक्षण नहीं हो सकता है, लेकिन गंभीर मामलों वाले लोग दैनिक गतिविधियों को करने में असमर्थ हो सकते हैं। कुछ सबसे सामान्य लक्षण हैं:
<उल शैली = "सूची-शैली-प्रकार: डिस्क;">स्पोंडिलोलिस्थीसिस के कई कारण हैं, उनमें से कुछ हैं:
<उल शैली = "सूची-शैली-प्रकार: डिस्क;">
पैथोलॉजी:>
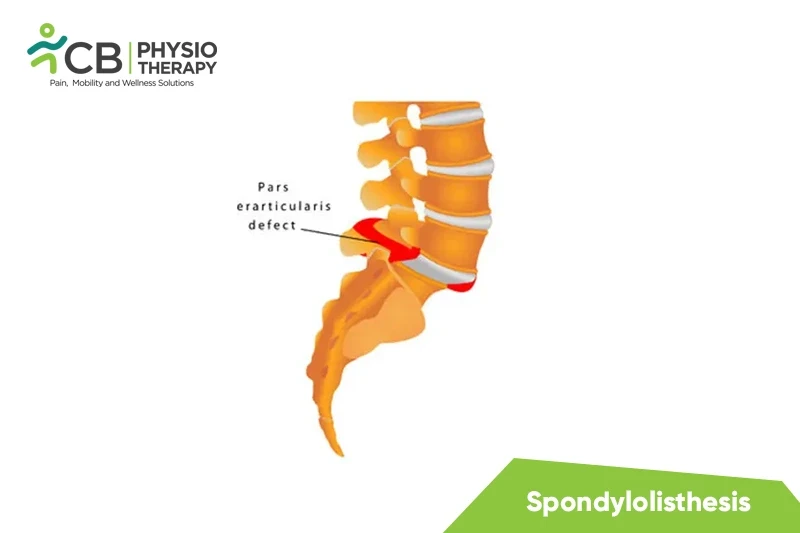
स्पोंडिलोलिस्थीसिस की विकृति में काठ कशेरुकाओं का एक खंडित पार्स इंटरर्टिक्युलेरिस शामिल होता है, जिसे इस्थमस भी कहा जाता है। यह कशेरुकाओं की सहायक अखंडता को प्रभावित करता है, जिससे कशेरुकाओं के कॉर्पस की फिसलन हो सकती है, जिसे स्पोंडिलोलिस्थीसिस कहा जाता है। यह, बदले में, काठ की अस्थिरता की ओर जाता है। यह स्लिपेज 2 दिशाओं में हो सकता है: एंटीरियर ट्रांसलेशन, जिसे एंटेरोलीस्थेसिस कहा जाता है, या बैकवर्ड ट्रांसलेशन, जिसे रेट्रोलिस्थेसिस कहा जाता है। त्रिकास्थि, L4 और L5 के बीच की तुलना में मजबूत हैं, जिसके कारण L4 में कशेरुक स्लिप आमतौर पर विकसित होती है।
शारीरिक परीक्षा:
शारीरिक परीक्षा इस स्थिति के निदान में पहला कदम है। स्पोंडिलोलिस्थीसिस के मामले में, साधारण व्यायाम के दौरान रोगी को पैर को सीधे बाहर की ओर उठाने में कठिनाई हो सकती है।
X-rays:
निचली रीढ़ की एक्स-रे का उपयोग यह निर्धारित करने के लिए किया जाता है कि कशेरुका जगह से बाहर तो नहीं है। परीक्षक एक्स-रे छवियों पर हड्डी के किसी भी संभावित फ्रैक्चर की तलाश भी कर सकता है।
CT-scan:
सीटी स्कैन गलत हड्डी की नसों पर दबाव डालने की अधिक विस्तृत छवि दिखाता है।
मैग्नेटिक रेजोनेंस इमेजिंग (MRI):
चुंबकीय अनुनाद इमेजिंग (MRI) स्कैन से दबी हुई नसों का पता लगाने में मदद मिलती है।
दवा: भड़काऊ दवाएं जैसे इबुप्रोफेन, एपिड्यूरल स्टेरॉयड इंजेक्शन आदि।
ध्यान दें: डॉक्टर के नुस्खे के बिना दवा नहीं लेनी चाहिए।
सर्जरी:>
स्पोंडिलोलिस्थीसिस का उपचार दर्द की गंभीरता और कशेरुकाओं के खिसकने पर निर्भर करता है। स्पोंडिलोलिस्थीसिस के गंभीर मामलों से पीड़ित वयस्क स्पाइनल फ्यूजन सर्जरी करानी पड़ सकती है। खोई हुई कशेरुकाओं के सर्जिकल सुधार की आवश्यकता तब होती है जब हड्डी इतनी नीचे खिसक जाती है कि रीढ़ गैर-सर्जिकल उपचारों का जवाब नहीं देती है। अगर रीढ़ की हड्डी की नसों पर दबाव पड़ रहा हो तो सर्जरी की भी जरूरत पड़ती है।
थर्मोथेरेपी सर्कुलेशन बढ़ाकर और दर्द कम करके राहत प्रदान करती है।
क्रायोथेरेपी का उपयोग गले की मांसपेशियों के लिए राहत प्रदान करने के लिए किया जाता है।
अल्ट्रासाउंड थेरेपी ध्वनि तरंगों को पारित करके काम करती है जिससे ऊतक एक आवृत्ति पर दोलन करते हैं जो रक्त प्रवाह को बढ़ाता है।
ट्रांसक्यूटेनियस इलेक्ट्रिकल स्टिमुलेशन (TENS):
यह विद्युत साधन विद्युत प्रवाह की चर तीव्रता के माध्यम से मांसपेशियों को उत्तेजित करता है। TENS मांसपेशियों की ऐंठन को कम करने में मदद करता है और शरीर के एंडोर्फिन (प्राकृतिक दर्द निवारक) के उत्पादन को बढ़ाता है।
इंटरफेरेंशियल थेरेपी (आईएफटी):
IFT रक्त परिसंचरण को बढ़ाने में मदद करता है, रीढ़ की हड्डी को उत्तेजित करता है, और दर्द और सूजन को कम करता है।
ब्रेस:>
राहत के लिए अस्थायी रूप से ब्रेस का उपयोग किया जा सकता है। हालांकि, लंबे समय तक ब्रेस पहनने से मांसपेशियां कमजोर हो सकती हैं।
दर्द को कम करने, रक्त के प्रवाह को बढ़ाने, सूजन को कम करने, ऊतक वृद्धि को बढ़ावा देने, और मांसपेशियों की ऐंठन से राहत प्रदान करने के लिए मालिश उचित दबाव के प्रयोग का उपयोग करती है।
मैनुअल थेरेपी दर्द को कम करती है, और इस प्रकार गति की सीमा को बढ़ाकर कार्य में सुधार करती है, उदाहरण के लिए, हेरफेर, गतिशीलता, आदि।
व्यायाम:>
व्यायाम में गति की एक सरल श्रेणी शामिल है, जैसे मोड़, विस्तार, पार्श्व मोड़, और घूर्णन गति। अकड़न और दर्द को कम करने के लिए स्ट्रेचिंग एक्सरसाइज की जाती हैं। और लम्बर स्पाइन का लचीलापन भी बढ़ाता है। पीठ की मांसपेशियों की खोई हुई ताकत को वापस पाने के लिए मजबूत बनाने वाले व्यायामों की सलाह दी जाती है। इन अभ्यासों में आइसोमेट्रिक व्यायाम, आइसोटोनिक व्यायाम, और बहुत कुछ शामिल हैं।
रोगी को बैठने और खड़े होने की गतिविधियों के दौरान रीढ़ की हड्डी के संरेखण को बनाए रखने की सलाह दी जाती है, न कि लंबे समय तक एक ही स्थिति में रहने के लिए अवधि, और इसलिए बीच में ब्रेक लें। स्पोंडिलोलिस्थीसिस के लक्षणों से राहत पाने के लिए चिकित्सा हस्तक्षेप महत्वपूर्ण है। इस स्थिति के अधिकांश लक्षणों को कम करने के लिए शुरुआती उपचार के उपायों की सलाह दी जाती है, क्योंकि अगर अनुपचारित छोड़ दिया जाए तो यह दर्द और स्थायी क्षति का कारण बन सकता है।
फिजियोथेरेपी के बारे में हमारे विशेषज्ञों को खोजने और उनसे जुड़ने के लिए अपने शहर का चयन करें स्पोंडिलोलिस्थीसिस