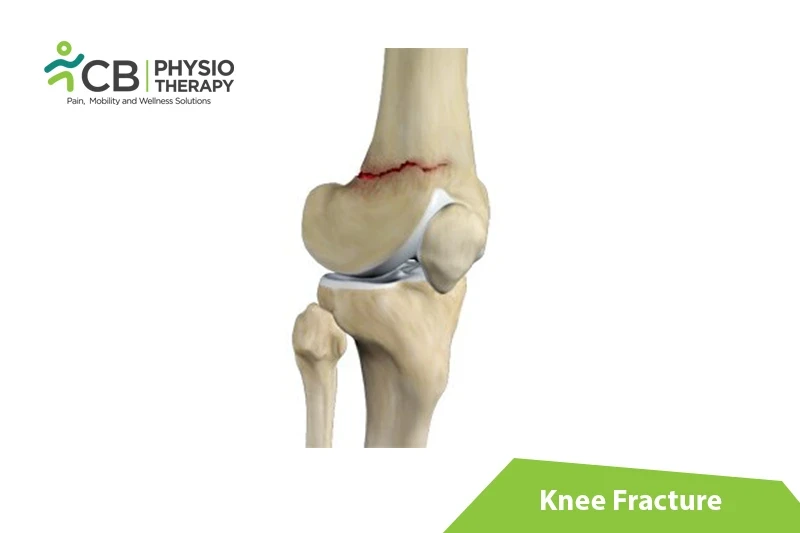
A knee fracture is a break or a crack in the bones that form a knee joint. These bones can get injured by a fall, traffic accident, contact sports, and physical exercises. The most common form of knee fracture is a patellar fracture, though knee fracture can involve any bone in the joint, including the patella, tibial plateau, tibial tuberosity, tibial eminence, and femoral condyles. Fracture in the knee joint can either be an isolated fracture, i.e single bone, or multiple fractures, which involve other knee-joint parts like the patella, femur, and tibia.
Types of Knee Fractures
Knee fractures can occur in any part of the bones. Types of knee fractures include:
Hairline fracture:
The hairline fracture occurs on the bone's surface and does not penetrate through the entire thickness of the bone. The hairline fracture cannot spread through the whole bone, it covers the knee bone partially and is treated with the help of conservative treatment.
Stable Fracture or non-displaced fracture:
In a stable fracture, the pieces of the bone remain fully aligned or the broken ends are separated by only a millimeter or two. In a stable fracture, the bones often stay in place during healing.
Displaced Fracture
In a displaced fracture, the bone fragments are separated and are not aligned properly. This type of fracture requires surgery, so that the pieces of bone are put back together.
Comminuted Fracture
This type of fracture has three or more shattered bone parts. And therefore, the knee is very unstable.
Open Fracture
In an open fracture, the skin is broken and the bone is exposed. This type of fracture can cause osteomyelitis or soft tissue infection. Open fractures often involve severe damage to the surrounding muscles, ligaments, and tendons and require immediate care.
Depending on the type and severity of fracture, symptoms vary, these may include:
Pathology:
Knee joint fractures are caused by falls, accidents, sharp blows, or bone infections, which the knee fails to resist causing a break or fracture. They can usually involve nerves, ligaments, muscles, and tendons.
The causes of knee fractures can be varied, they may occur due to:
Physical Examination:
The examiner checks the detailed medical history and also examines the knee to check the sensation and muscle strength. The examiner also checks for hemarthrosis, a condition in which the blood from the fractured knee collects inside the joint area, causing swelling and intense pain.
X-ray:
X-ray shows images of dense structures, such as broken pieces of bone, and also helps in determining the involvement of the knee or ankle joint, and also finds out the gap between broken bones.
Computed Tomography scan (CT scan):
A computed tomography scan (CT scan) uses X-rays and a computer to make detailed images of the injured knee.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) uses magnets, radio waves, and a computer to make detailed images of the knee to help the doctor make a diagnosis.
Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn), Motrin, Naproxen, Daypro, and Celebrex etc..
NOTE: Medications should not be taken without the doctor's prescription.
Surgery:
When conservative methods fail to work and also in cases where the bones are displaced, surgical techniques are used, such as using screws, plates, metal pins, or knee arthroscopic surgery. Arthroscopic surgery is used to treat non-displaced and hairline fractures not responding to conservative treatment and is also performed to repair the tendon and ligamental tears associated with fracture.
Rest:
Cast and braces are used to hold the ends of the bone together in position. During recovery, the knee is immobilized with a brace. Knee braces can also be used if the patient suffers from chronic stiffness or weakness in the joint, a knee brace can be continued for support. It helps to stand and move around with more confidence.
Cryotherapy involves the direct application of ice covered with plastic or cloth kept over the knee joint for around 30 minutes, two to three times a day.
Thermotherapy or moist heat is applied to the knee joint, its increases blood circulation.
Assistive devices:
Assistive devices including, a wheelchair, crutches, cane, or walker can be used for support.
Ultrasound therapy helps to break the adhesions and thus increases the range of motion and decreases pain.
Transcutaneous electrical stimulation (TENS):
TENS is used to reduce pain and swelling in the knee. And also helps to improve the strength of the muscle.
Laser therapy (LLLT):
Laser therapy enhances the healing process and accelerates callus formation.
Range of motion exercises:
Simple range of motion exercises are done in the pain-free range to increase joint movement such as knee flexion, knee extension, SLR, etc.
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises:
Stretching exercises are done to achieve more range of motion and flexibility. Strengthening exercises include isometrics, isotonic, isokinetic exercises for quadriceps, hamstring, adductor, abductor, gluteal, ankle muscles, etc. Progressed to resisted exercises with therabands and weights.
Weight Bearing:
Weight-bearing exercise is initially limited to gently touching the floor with the toe, with the help of a walker, crutches, or cane. As the knee heals, the muscles strengthen, and gradually more weight is put on the leg.
Balance and proprioception exercises:
Balance and proprioception exercises can be done with a bobath ball or on a wobble board.
The patient is advised to play physical sports with care, to minimize the possibility of reoccurrence of knee fracture. The patient is also advised to avoid stairs, squatting, and bending, to limit stress on the knees. And also should follow physiotherapy even after the fracture is healed, to restore muscle strength and range of motion.
Select your City to find & connect with our experts regarding Physiotherapy for Knee Fracture