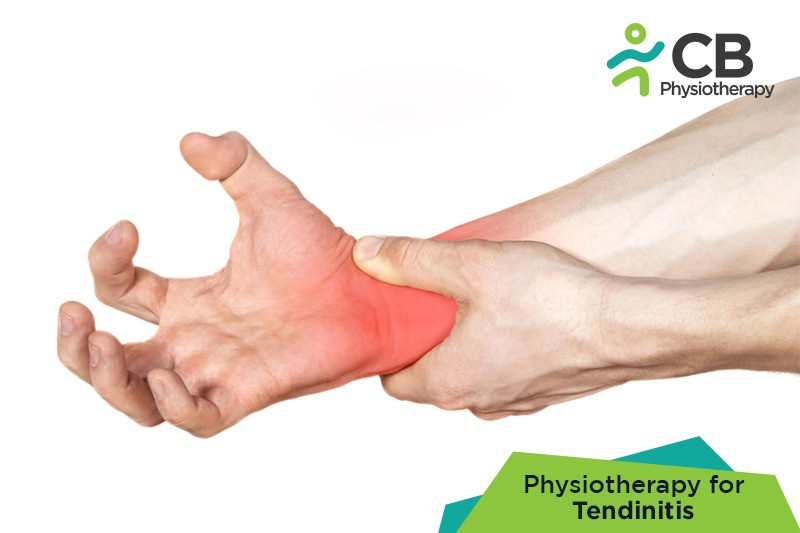
Tendinitis or tendonitis is the inflammation of a tendon, which is a fibrous band of tissue that connects the bones to muscles. Tendonitis is a condition in which the tendon becomes inflamed or suffers a tear, causing acute pain, tenderness, and inflammation making it difficult to move the affected joint. The most commonly affected parts of the body are the elbow, wrist, finger, thigh, and ankle, etc. Tendinitis can occur more commonly among adults who play a lot of sports and occurs in any age group. Though older people are more susceptible because the tendons tend to become weaker with age. Some of the common Tendinitis that commonly occur in our body are:
Achilles tendinitis: Achilles tendon lies between the heel and the calf muscle. Occurs most commonly in sports players. Usually caused due to improper footwear. It is mostly seen among patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Peroneal Tendonitis: Peroneal tendonitis affects the two tendons, one tendon attaches to the little toe, while the other runs along the sole and attaches to the inner side of the arch. If they can rub against the bone and overuse and load, symptoms are caused like pain and instability.
Posterior Tibial Tendonitis: Posterior Tibial Tendonitis affects the tendon that attaches the back of the shinbone to the foot. When it becomes inflamed, over time, this can result in flatfoot.
Supraspinatus tendinitis: Tendon around the shoulder joint becomes inflamed, causing supraspinatus tendinitis, which causes pain, especially during upward movement and becomes more painful while lying on the affected shoulder at night.
Tennis or golfer’s elbow: Lateral epicondylitis also known as tennis elbow, the patient feels pain on the outer side of the elbow radiating down towards the wrist. Whereas in Golfer’s elbow or medial epicondylitis pain is on the inner side of the elbow, commonly occurring among Golfers. Pain is more acute when the patient tries to lift against a force, radiating down to the wrist.
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis: It is the inflammation of the sheath that surrounds the thumb and lies between the thumb and wrist. It becomes painful to move the thumb due to the thickening of the sheath and swelling in the area.
Trigger finger or thumb: The tendon sheath in the palm is thickened and inflamed thus becomes fixed in a bent position and does not allow the tendon to move smoothly. Even sometimes a nodule forms along the tendon. The finger or thumb clicks when straightened.
Tendinitis of the wrist: Occurs most commonly in players like badminton players, tennis players, and workers, due to repeated use of the wrist.
Jumper's knee: It is a form of knee tendonitis, involving either the quadriceps tendon at the upper edge of the kneecap or the patellar tendon at the lower edge of the kneecap. Occurs especially in basketball players and distance runners due to overuse.
Most commonly the patients suffering from tendinitis have the following symptoms in the tissues surrounding the joint. These symptoms worsen after overuse:
Patients suffering from the following Tendinitis suffer from pain in the specific regions correspondingly:
Repetitive action is the most common cause of tendonitis. Due to the increased frequency of the same motion while working or playing sport. Tendinitis can also result from:
For the diagnosis the physician does the physical examination, while moving the tendon, a creaky sound may be heard, due to inflammation and thickening of the tendon. Tenderness at one specific point in the tendon, indicates tendinitis.
X-ray
X-ray can show the calcium deposits around the tendon thus help to confirm tendinitis.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): may reveal swelling of the tendon sheath thus helps in the diagnosis.
Medications: Pain relievers, Corticosteroids etc
Note: Duly Prescribed by the Practitioner.
Ultrasonic treatment. It is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a small incision to insert a device to remove the tendon scar tissue with ultrasonic sound waves.
Surgery. Surgical repair may be needed, depending on the severity of the tendon injury especially if the tendon has torn away from the bone.
Physical therapy:
The therapist first recommends Rest, Ice Packs, compression, and elevation, followed by the use of modalities and different techniques in reducing irritation to the tendon.
Dry Needling is also one of the treatment methods which helps reduce muscle tightness around the involved tendons.
Cryotherapy reduces inflammation and swelling causing a decrease in pain, around the tendon. It also reduces nerve activity (temporarily), which can also relieve pain.
Thermotherapy is used to promote vasodilatation, accelerates healing, decreases spasm, resulting in a decrease in pain, and promotes relaxation.
Ultrasound therapy helps in treating tendinitis by promoting tendon healing.
Shock-wave therapy is commonly used for the management of tendinitis. It stimulates metabolic activity by promoting tissue healing and also affects the nociceptors thus decreases pain.
Massage:
Massage can help promote healing when used in combination with exercises.
Exercises programs:
Stretching exercises can reduce muscle spasm and helps lengthen the tendon. Eccentric exercises are very effective for tendinitis, stimulating the tendon’s internal repair system, and also helps restore strength and flexibility.
Education about appropriate activities:
Education is an important part of treatment. Education of the patient to correct body mechanics and posture help reduce the strain on a tendon under stress due to repetitive activities.
Select your City to find & connect with our experts regarding Physiotherapy for Tendinitis