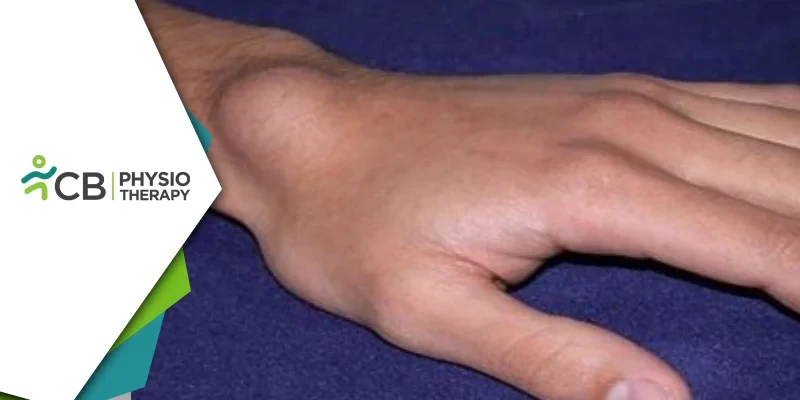
Ganglion cysts are benign, fluid-filled lumps that commonly appear along the tendons or joints of the wrists or hands. Although generally non-cancerous and harmless, they can cause discomfort, pain, and functional impairment. This blog delves into the nature of ganglion cysts, their causes, symptoms, and the crucial role that physiotherapy plays in managing this condition.
Understanding Ganglion Cyst
A ganglion cyst is a small sac of fluid that forms over a joint or tendon, usually on the wrist or hand. The fluid inside the cyst is similar to the synovial fluid found within joints, which helps lubricate and cushion them during movement. These cysts can vary in size, sometimes becoming more prominent with repetitive activity and shrinking when the hand is at rest. The exact cause of ganglion cysts is not entirely understood, but several factors may contribute to their development like repeated stress or irritation of a joint or tendon can lead to the formation of a cyst. Single injury or repetitive micro-traumas can trigger the formation of a ganglion cyst. The symptoms include a noticeable bump on the wrist or hand that can vary in size and may fluctuate in size. The cyst can press on nearby nerves, causing pain, tingling, or numbness. Activities involving the wrist or fingers can become uncomfortable or painful, particularly if the cyst is large or pressing on a nerve.Role of Physiotherapy in Managing Ganglion Cysts
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the conservative management and post-surgical rehabilitation of ganglion cysts. It focuses on reducing symptoms, improving function, and preventing recurrence through various therapeutic strategies.1: Pain Management
Physiotherapists employ several techniques to alleviate pain caused by ganglion cysts:
2: Electrotherapy:
Methods like TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation), Laser therapy, etc, can help reduce pain by sending electrical impulses through the skin to the nerves.
3: Ice Therapy:
Applying ice to the affected area can reduce inflammation and pain, particularly after activities that may aggravate the cyst.
4: Improving Mobility and Function
Restricted movement and discomfort in the hand or wrist can be addressed through:
5: Manual Therapy:
Techniques like joint mobilization and soft tissue manipulation can improve range of motion and reduce stiffness. This hands-on approach helps to ensure that the joints and surrounding tissues remain flexible.
6: Stretching and Strengthening Exercises:
Specific exercises target the muscles and tendons around the cyst to improve flexibility and strength. This can help maintain joint stability and reduce the likelihood of recurrence.
Activity Modification and Ergonomics
Physiotherapists guide modifying activities to reduce strain on the affected joint or tendon:1: Ergonomic Adjustments:
Recommendations on hand positioning and equipment use to minimize stress during daily activities. This includes adjusting computer workstations, using ergonomic tools, and altering hand positions during tasks.
2: Activity Modification:
Techniques to modify the way tasks are performed to avoid aggravating the cyst. For example, changing the way one grips objects or performs repetitive tasks.
Preventing Recurrence
Recurrent ganglion cysts can be frustrating, but physiotherapy can help minimize the risk:1: Maintenance Exercises: Ongoing exercises to maintain flexibility and strength in the hand and wrist, which are crucial for joint health.
2: Education: Teach patients about joint protection strategies, such as proper body mechanics and the importance of regular exercise, to prevent future issues.
Ganglion cysts on the hand, while generally benign, can cause discomfort and interfere with daily activities. Understanding the nature of these cysts, their causes, and symptoms is crucial for effective management. Physiotherapy offers a non-invasive, effective approach to managing ganglion cysts, focusing on pain relief, improving function, and preventing recurrence. Through a combination of therapeutic techniques, ergonomic adjustments, and patient education, physiotherapists play a vital role in helping individuals manage and recover from ganglion cysts, enhancing their quality of life.
By integrating physiotherapy into the management plan for ganglion cysts, patients can achieve better outcomes, reduce pain, and improve their overall hand function, enabling them to return to their daily activities with greater ease and comfort.