Relaxation Techniques:
Physiotherapists may teach relaxation techniques such as progressive muscle relaxation, guided imagery, or mindfulness exercises. These techniques help reduce anxiety, tension, and breathlessness associated with dyspnea.
Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES):
NMES is a technique that uses electrical currents to stimulate specific muscles or muscle groups. By applying electrical impulses to the respiratory muscles, such as the diaphragm or intercostal muscles, NMES can help strengthen these muscles and improve respiratory function.
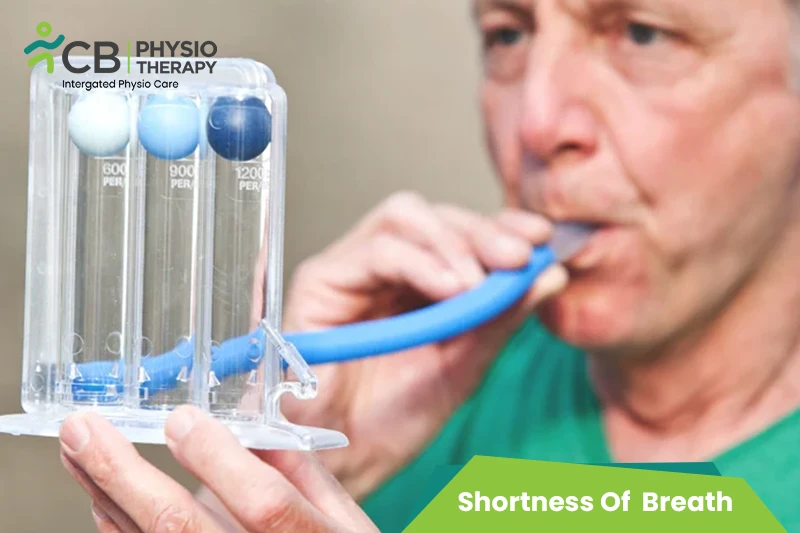
Inspiratory Muscle Training (IMT) Devices:
These devices use electrical resistance or pressure thresholds to provide resistance during inhalation. They help strengthen the muscles involved in breathing, primarily the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, thereby improving respiratory efficiency and reducing dyspnea.
Chest Wall Oscillation Devices:
These devices deliver high-frequency oscillations to the chest wall through electrical currents or mechanical vibrations. They help mobilize mucus and secretions in the airways, aiding in their clearance and reducing breathlessness.
High-Frequency Chest Wall Compression Devices:
These devices use electrical impulses to deliver rapid compressions to the chest wall. The oscillations generated help loosen mucus and improve airway clearance.
Breathing Exercises:
Physiotherapists teach various breathing techniques to optimize lung function, improve ventilation, and reduce dyspnea. These exercises may include diaphragmatic breathing, pursed-lip breathing, and controlled breathing patterns.
Airway Clearance Techniques:
Physiotherapists employ techniques to help mobilize and clear excessive mucus or secretions from the airways. This can include techniques such as postural drainage, percussion, vibration, coughing techniques, and active cycle of breathing techniques.
Manual Techniques:
Physiotherapists may use manual techniques to improve respiratory mechanics and lung expansion. These techniques may involve gentle mobilization of the rib cage, chest wall stretches, and manual assistance with breathing exercises.
Exercise Training:
Physiotherapists prescribe individualized exercise programs to improve cardiovascular fitness, respiratory muscle strength, and overall endurance. This may include aerobic exercises, strength training, and specific respiratory muscle training.
Posture and Positioning:
Optimal posture and positioning can enhance lung capacity and breathing mechanics. Physiotherapists provide guidance on proper posture and recommend specific positions that can facilitate better breathing.
Cardiovascular Endurance Training:
Depending on the individual's overall fitness level and specific needs, physiotherapists may incorporate cardiovascular endurance training, such as stationary cycling or treadmill walking, to improve stamina and reduce breathlessness during physical activity.