Coronavirus has reached its deadly stage. It has been observed that patients suffering from COVID-19 have difficulty in breathing which causes a rapid decrease in their blood oxygen levels. Usually, the symptoms of this disease are visible after the lung gets damaged by 25%, resulting in a dip in oxygen saturation level to 80- 85%. In such a situation, an immediate oxygen supply is required. If oxygen is not available during this period, the patient may face complications. The cells in our body require at least 89% of oxygen saturation level while healthy individuals have a saturation level of 95 and above. Any significant drop in this level causes breathlessness. With an increased demand for oxygen supply, medical institutes are overburdened and also the availability of ventilators is limited. Therefore, the best way to reduce our dependency upon hospitals and ventilators can be achieved by managing blood oxygen levels at our homes by a natural method of proning. Proning is a technique used to optimize oxygenation, it is an easy-to-do home exercise. A method of attaining a prone position is required when the patient feels discomfort while breathing and also when the oxygen level decreases below 94. In this blog, we will discuss proning and how it increases your oxygen supply.
Proning or Prone positioning: Patients who are on ventilators due to pneumonia spend long hours lying on their back, due to which the fluid begins to enter the back of the lungs. The air breathed in cannot mix well with the blood flowing through the lungs. This is because of the pooling of fluid causing the lung tissue to collapse. The lung tissue in the back of the chest undergoes inflammation and infection-causing a decrease in the transfer of oxygen to the blood. The patient ultimately becomes tired of breathing and exhausted with the effort of keeping the blood completely oxygenated. The best way to support breathing is by keeping the patient on a ventilator. But ventilators can often damage the lungs. Therefore, a safe and simple method to improve oxygenation is by prone position or proning. Prone position or proning opens up the collapsed airways and increases blood oxygen levels. In a prone lying position, the heart rests on the breast bone giving space for the lungs to expand, this increases the airflow to the back, where the blood circulation is the most. So, both blood circulation and more oxygen, lead to effective oxygenation.
Positioning: The patient lies in a prone posture on their abdomen or on their belly by facing down towards the bed. Keep a pillow below the neck and chest. Keep two pillows below each shin. Make sure that the patient lies comfortably, if not so the patient might feel suffocated. Do not spend more than half an hour in each position.
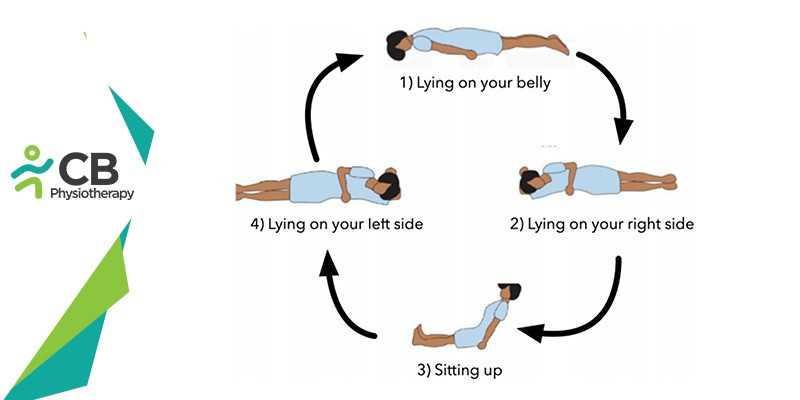
- Lying on your stomach: Begin by lying on a bed by stomach facing towards the bed for 30 minutes.
- Side-lying position to the right side: For side-lying, lie on your right side for 30 minutes.
- Sitting up: Sit up in the bed with your back supported and both legs extended for 30 minutes.
- Side-lying position to left side: While lying in the bed lie on your left side for 30 minutes.
- Lying on your stomach: Return to lying on your stomach by facing toward the bed for 30 minutes.
Benefits
- It is a safe and simple home method to improve oxygenation.
- It improves ventilation.
- Helps the body to get air into all areas of the lungs.
- Prevents worsening of complications due to decreased oxygen circulation.
- Delays the use of mechanical ventilators by maintaining the supply of oxygen to the body tissues.
Safety Measure
- Avoid prone position or proning immediately after meals.
- Maintain prone position till the patient feels comfortable.
- Pillows should be kept under pressure areas, especially around bony prominences.
Contraindications
Prone position should be avoided in conditions like:
- Pregnancy.
- Deep venous thrombosis.
- Major cardiac conditions.
- Fractures like spinal, femoral, or pelvic fractures.