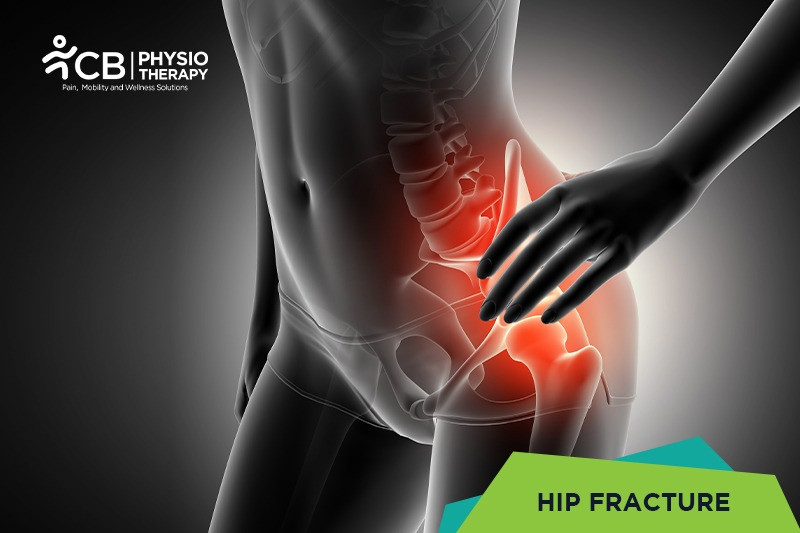
The hip joint comprises the femur i.e. the thigh bone and the pelvic bone. Hip fracture occurs when there is a break or a crack in the upper part of the thigh bone.
Types:
A broken hip can occur due to multiple reasons, some of the causes are mentioned below:
Patients with broken hip experience extreme pain. Other symptoms associated with a broken hip are as below:
Pathology:
Hip pathology is a break in the upper part of the femur, commonly related to osteoporosis. The patients usually have progressive pain, not relieved by rest.
Physical examination:
Physical examination is done to check for pain, swelling, and tenderness in the affected hip.
X-rays:
X-rays help to determine the location and severity of the fracture.
CT scan:
CT scan is used to examine internal injuries like car accidents or other types of trauma.
MRI:
MRI is done to check the joint abnormalities caused by repetitive trauma or repetitive injuries, to the muscles, bones, cartilage, or ligaments.
Medication: Anti-inflammatory, Antibiotics, Analgesics
Note: Medication should not be taken without the doctor's prescription.
Surgery: Surgery depends on the type of fracture, most commonly performed operations are:
Rest:
The patient should take bed rest to enhance the process of healing. Avoid walking or moving around as the healing process takes time and attempting to walk could slow down the process.
Ice compressions:
Apply an ice pack over the swollen area for 5-10 min to ease the pain and help reduce the inflammation.
Heat therapy is recommended over the affected area to improve blood circulation and make the joints more flexible.
Transcutaneous Electrical stimulation (TENS):
Transcutaneous Electrical stimulation (TENS) is used to help improve muscle reeducation, improve the fracture healing process with minimal thermal effects.
Scar massage and mobilization:
Scar massage and mobilization are given to help reduce scar adhesion after surgical intervention.
Mobility exercises:
Mobility exercises like hip extension, overhead arm extension, standing diagonal reach, modified get up and go, heel raises onto toes, double arm lifting, repeated chair stands, stepping up and down, calf raises with both legs or one leg, lunges- forward and back
The patient is made to walk on the parallel bars or with a walker or cane. A stationary bicycle for 10 - 15 minutes is recommended. Progressive weight-bearing is continued as tolerated by the patient. For patients with internal fixation, partial weight-bearing should start for 8 - 10 weeks and full weight-bearing after 3 months. For walking weight-bearing technique used is:
Non-Weight Bearing – No body weight is placed through the affected limb.
Minimal Weight Bearing –25% of the weight is put through the affected limb by heel-toe walking.
Partial Weight Bearing – 50% of the weight is put through the affected limb by heel-toe walking.
Full Weight Bearing – 100% of the weight is put through the affected limb by heel-toe walking.
For staircase climbing:
Hold the railing with one hand and the crutch in the other, while going upstairs take one step at a time. Go up with the unaffected leg, while coming downstairs take one step at a time, bring the affected leg down first.
Low-intensity exercises, help to regain lost joint strength and flexibility. Strengthening exercises can be done with weights, resistance bands, or other equipments to improve strength and mobility of the muscles and joints in and around the fractured. Weight-bearing immediately after surgery is recommended to prevent the complications of pressure sores, atelectasis, pneumonia, deconditioning, and thromboembolism. Strengthening exercises like ankle exercises briskly and regularly bend the ankles up and down, buttock exercises like tightening the buttock muscles by squeezing them together. Thigh exercises like sitting with the legs out in front, pulling the toes up, and pushing the knee down onto the bed, tightening the thigh muscles. Hip abduction by lying on the bed with legs out in front, keeping knee straight and toes pointing towards the ceiling, sliding the leg out to the side, leading with the heel, and bringing it back to the middle.
Stretching exercises:
Stretching exercises are performed regularly to improve the flexibility of the joints and muscles. Internal rotation from hip flexion is stressful for joint, straight leg raise can provoke irritation to the nerve, also impact activities should be avoided few weeks.
Physiotherapy aims to improve muscle strength, walking safety, and efficiency and educate the patient for its prevention. Modifications at home to prevent falls and follow exercises regularly to slow bone loss and maintain muscle strength, balance, and coordination.
Select your City to find & connect with our experts regarding Physiotherapy for Hip Fracture