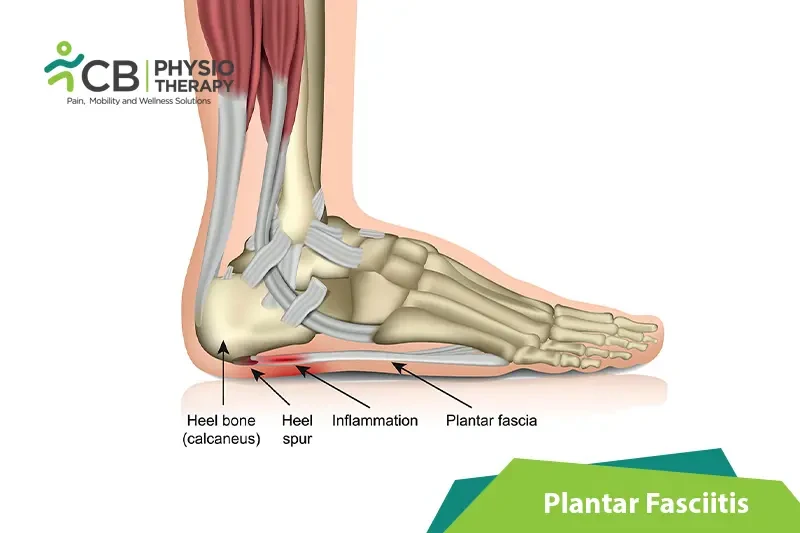
Plantar fasciitis is the inflammation of the ligament (bowstring) or plantar fascia, present underneath the sole attached at the heel, responsible for stretching.
Patients with plantar fasciitis suffer from pain and inflammation. The symptoms of plantar fasciitis include:
Excessive pressure on the foot can cause a small tear in the tissue and too much pressure can damage the plantar fascia. Other causes may include:
Pathology
Plantar fasciitis occurs when the plantar fascia becomes irritated. The plantar fascia supports the foot, providing a tension bridge as well as shock absorption, but it cannot take too much pressure, as a result, excessive tension creates fascia fibers to become inflamed.
Physical examination:
To check the tenderness, redness, swelling, and exact location of the pain in the foot. Examination for reflexes, muscle tone, sense of touch and sight, coordination, and balance are also done.
X-ray:
An X-ray can be used to check any bony lesions of the foot like subcalcaneal spur.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used for assessing plantar fascia thickening.
Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), Corticosteroids etc.
Note: Medication should be taken as prescribed by the doctor.
If the conservative treatments do not relieve the symptoms of plantar fasciitis, then the next option is surgery.
Rest:
Rest is first recommended for plantar fasciitis until the inflammation goes away.
Ice:
Ice packs or ice massage can be applied for the treatment of plantar fascia, it is done for 15 to 20 minutes.
Contrast Bath:
A contrast bath is used for the reduction of swelling and inflammation, given for 15 min.
Shock wave therapy:
Shock wave therapy is sound waves bombarded on the heel to stimulate healing within the ligament and relieve symptoms.
Ultrasound:
Ultrasound is given to decrease inflammation, pain and prevent adhesion formation.
Iontophoresis:
Iontophoresis is done in which medication is allowed to pass through the tissue with the help of an electric current.
Posterior-night splints:
Posterior-night splints help maintain ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension, thus providing constant stretch on the plantar fascia.
Foot orthoses:
Foot orthoses provide short-term functional benefits and also a reduction in pain.
Shoe modification:
A soft silicone heel pad can be used to protect the heel. Heel cushions are placed in the back of the shoe, which reduces the effect of the arch support. A viscoelastic heel cup can be placed over the medial calcaneal tubercle to reduce ground reactive forces.
Sole Modification:
A sponge rubber cushion with the center removed may be placed under the heel, or a hole may be drilled into the sole of the shoe at the site of inflammation and covered with sponge rubber.
Taping:
Taping can be done on the gastrocnemius and plantar fascia.
Strengthening exercises:
High-load strength training is an effective treatment for plantar fasciitis. It helps in the reduction of pain and improves function. Towel curls, towel pickup, calf raises (unilateral and bilateral), picking up marbles, and resisted thera-band exercises for the lower leg are examples of strengthening exercises.
Stretching exercises:
Stretching consists of crossing the affected leg over the unaffected leg and using the fingers across the base of the toes to apply pressure onto the toe extension until a stretch is felt along the plantar fascia. Achilles tendon stretching exercises can be performed in a standing position with the affected leg placed behind the unaffected leg with the toes pointed forward. The front knee is bent, keeping the back knee straight and heel on the ground. The stretching can be gentle, prolonged, slow, and static, performed five times by holding each stretch for 15-20 sec.
Manipulations and mobilization:
Manipulations and mobilization help in decreasing pain and stiffness, e.g ankle, subtalar and midfoot joint mobilizations.
Depending on the stage of injury patients should be educated that the symptoms may take a few weeks to improve injury. The patient should follow the advice and activity modification should be done to decrease the distance and duration of walking and instead of doing running or, jumping activities, swimming or cycling should be done to reduce the stress on the foot.
Select your City to find & connect with our experts regarding Physiotherapy for Plantar Fasciitis