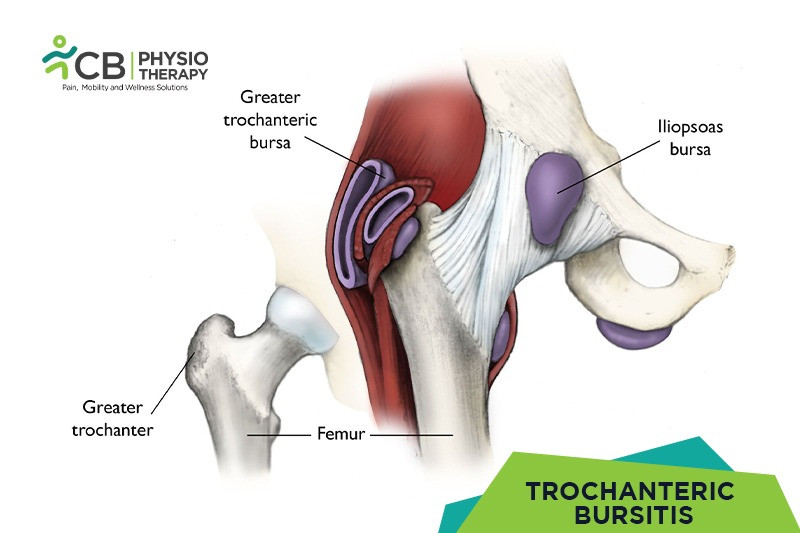
Trochanteric bursitis is the inflammation and swelling of the greater trochanter bursa, a bursa is a fluid-filled sac that allows the tissue to slide over one another. Bursa is at the outside of the hip, ie the greater trochanter has a bursa called the trochanteric bursa.
The trochanteric bursa allows the gluteal muscles i.e. the muscles of the back and side of the hip to slide smoothly over the greater trochanter. Bursitis is normally caused by the:
Patient with trochanteric bursitis has pain in the hip and other symptoms like:
Pathology
Trochanteric bursitis is caused by the friction to the bursa, present between the great trochanter and the iliotibial band that runs along the external thigh.
Physical examination:
Physical examination of the hip is done to check tenderness and the areas around the bursa.
X-ray:
X-rays are done to rule out other conditions related to bone.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) helps to check the inflammation or collection of fluid in the bursa.
Medication: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroid Injections.
Note: Medication should not be taken without the doctor's prescription.
Surgery:
Surgery is done in case conservative treatment does not relieve the symptoms. Surgeries recommended are listed below:
Ice is applied to the affected area to reduce pain and inflammation.
Heat is applied to the area to increase blood circulation and remove the toxic substances.
Ultrasound therapy is used to increase blood flow, thus delivering more oxygen and nutrients to the damaged tissues and enhancing the healing process.
Kinesio-Taping is applied as compression is not possible in the hip area. Taping alleviates pain and decreases inflammation.
Transcutaneous electrical stimulation (TENS):
Transcutaneous electrical stimulation (TENS) is used to reduce and relieve hip pain.
Shock wave therapy is another modality used by physiotherapists to relieve pain and enhance the healing process.
Dry needling is done to reduce lateral hip pain and improve function in patients with greater trochanteric bursa.
Massage therapy like deep tissue massage is given to the muscles and connective tissues around the hip.
Range of motion exercises are done to increase the mobility and flexibility of the low back, hip, and knee joint, these exercises improve strength, flexibility, and core stability.
Stretching exercises:
Stretching exercises are given to decrease the tension and help restore the movement. Passive stretching is done for the muscles and connective tissues of the hip by the physiotherapist.
Manual therapy is a hand on technique given gently to move the muscles and joints, it helps to improve motion and strength.
Strengthening exercises are given to strengthen the weak muscle which might cause imbalance resulting in excessive strain at the greater trochanter. Progressive resistance exercises can be given for the core muscles and lower extremities. Strengthening exercises can be done by lying on a table or the bed or floor by lifting the leg while lying in different positions. Then advance by doing the exercises in a standing position eg, standing squats.
The patient is advised to take rest and avoid activities that aggravate the pain as it might irritate the bursa further, and possibly delay recovery. Additional padding can be done on the bed or avoid lying on the affected side while sleeping to reduce stress in the area.
Select your City to find & connect with our experts regarding Physiotherapy for Trochanteric Bursitis